Lab materials
- Slides: Conditional statements 2
Tasks
This lab has two base tasks, first one simulating a cash register and the second one simulating a store food scale. The first task is extended by an extra task, adding support for bonus point management.
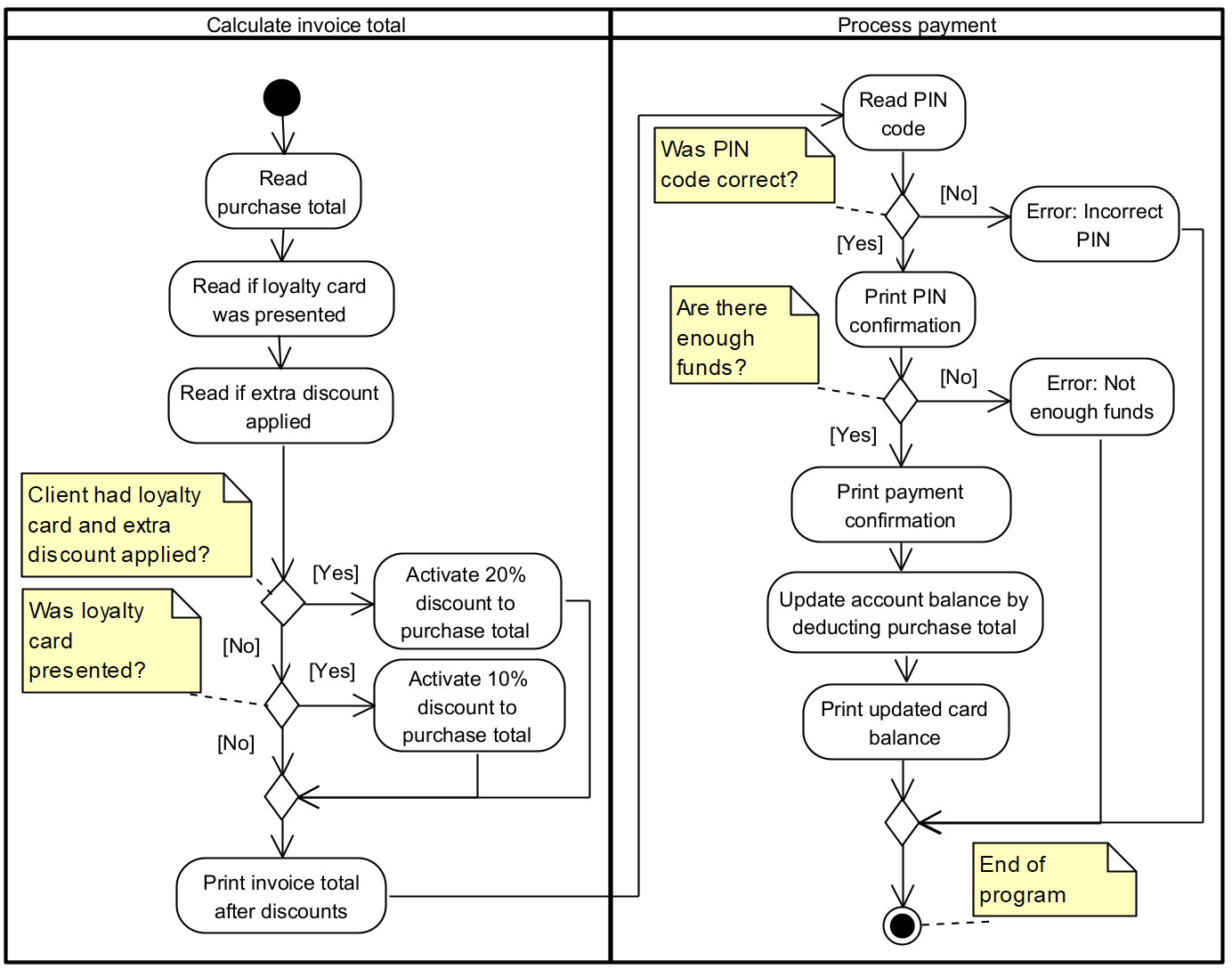
Task 1 [W02-1]: Cash register
With this task, we’ll create a simple cash register application with the goal of trying to compose different conditional statements. The task is provided with a starter code to start you off. Base your solution on the starter code, write your code statements after the comments specifying what to do!
Requirements:
- Program must be logically identical to the given algorithm
- Program must be built on the base code given. Your task is to add the missing printf , scanf , conditional statements and calculations. Use the code comments and the activity diagram as a reference.
- Don’t change the variable naming or the program structure
- Recommendation: To check that the values are correctly read and program behaves as expected, add printouts to check the variable values after mathematical operations.
Download task 1 starter code: [et] [en]
Algorithm
Testing
I’m proposing a series of tests for the program you are about to create. NB! I’ve left at least one important test case untested. Can you figure out which one?
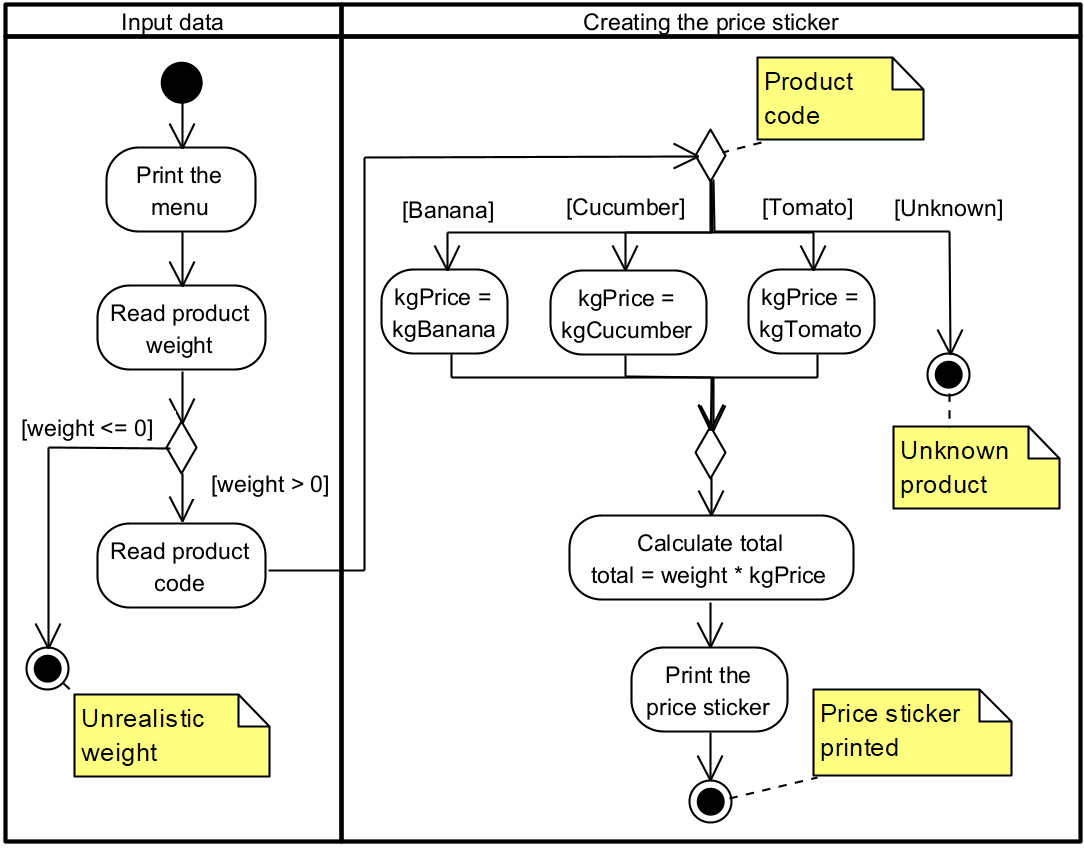
Task 2 [W02-2]: Food scale
In this task you will create a program, that simulates the food scale in a grocery store.
The UML activity diagram to structure your program on will be created in class. Your program must match or exceed the functionality described.
Requirements
- You must have at least four products available.
- Products are represented as pairs of product codes (integer) and names (e.g. 1 – banana).
- The user inputs an integer product code and a real numbered quantity (in kilograms) from the keyboard.
- You must handle matching the product code to the price of 1 kg in the switch statement.
- User will be displayed the total price only if a valid product code and weight are entered.
- The given price(s) must be given with 2 decimal places.
- Invalid product code and weight must trigger an error. There is no need to specify which error occurred. In case of an error, price must not be shown!
Download the starter code for task 2: 2_2_scale_base.c
Algorithm
A copy of the algorithm for those who either reach the second task more quickly during the lesson or lose their own copy of the algorithm. The algorithm will also be solved together in class with additional commentary
Testing
Test 1: Correct inputs will give us a total cost.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
Available products 1 - Banana 2 - Orange 3 - Lemon 4 - Tomato 5 - Cucumber 6 - Potato 7 - Apple 8 - Pear 9 - Plum Enter weight (kg): 2.5 Enter product code: 4 Selected product 4 - Tomato Entered weight: 2.5 kg Price per kilo 1.49 EUR Total price: 3.73 EUR |
Test 2: Invalid product code triggers an error.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Available products 1 - Banana 2 - Orange 3 - Lemon 4 - Tomato 5 - Cucumber 6 - Potato 7 - Apple 8 - Pear 9 - Plum Enter weight (kg): 2.1 Enter product code: 53 Error! Unknown product code! Exiting .. |
Test 3: Invalid weight triggers an error.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Available products 1 - Banana 2 - Orange 3 - Lemon 4 - Tomato 5 - Cucumber 6 - Potato 7 - Apple 8 - Pear 9 - Plum Enter weight (kg): -4 Error! Invalid weight! Exiting .. |
Extra task [W02-3]: Bonus account
The extra task is an extension of the first task. To do this, we’ll add an option for the user to use bonus points.
While solving the task, think carefully about everything that could go wrong at each stage of the transaction and how those issues are related!
Note: as a result of solving this task, you will end up with one long piece of spaghetti code — everything in a single function. We will start fighting against this from fourth week.
Requirements
- Add user’s bonus points count to the program, it should be initialized. Bonus points can only be integers (e.g., 1 bonus point, 15 bonus points).
- Before completing a transaction, the user is shown their total bonus points and the maximum number of points they are allowed to use for this purchase, according to the rules of using bonus point.
- Then the user is asked whether they want to use bonus points. If yes, the program asks how many they wish to use.
- Bonus point rules
- 1 bonus point equals 1 euro cent
- A maximum of 90% of the purchase can be paid with bonus points, calculated after discounts
- If the user enters a number of bonus points greater than what they have or greater than what is allowed for the purchase, the maximum permitted amount is used instead
- The rest of the transaction logic remains as specified by the base task
- At the end of the transaction, the user is shown the remaining balance of their bonus account
Necessary knowledge
- Know what is a truth table and how to read them
- Be able to form conditional statements consisting of multiple conditions
- Know what De Morgan’s law is and how to apply it
- Know how to use inversion and short forms for conditional statements
- Be able to initialize integers and floating point values when declaring them
- Be able to write nested conditional statements
- Be able to alter the variable value relative to the old value, on the same line
- Be able to use and print floating point values while specifying number of decimal places
- Understand how switch statements work and how to use them in code
- Be able to model a switch statement in an activity diagram
- Know how to use swim lanes
- Know how to have multiple different endings in both programs and in activity diagrams
Additional content
- De Morgan’s Laws
https://brilliant.org/wiki/de-morgans-laws/ - C/C++ if else if ladder with Examples
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-c-if-else-if-ladder-with-examples/ - Decision Making in C / C++ (if , if..else, Nested if, if-else-if )
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/decision-making-c-c-else-nested-else/ - Exit codes in C/C++ with Examples
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/exit-codes-in-c-c-with-examples/ - Beej’s guide: switch statement
https://beej.us/guide/bgc/html/split/variables-and-statements.html#switch-statement - Switch Statement in C/C++
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/switch-statement-cc/